| THYROIDECTOMY |
|
|
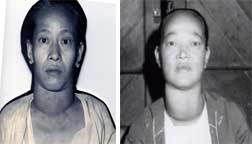
A large, firm, nodular goitre with possible retrosternal or retropharyngeal extension and the existence or threat of pressure phenomina , specially indicate the need for surgery. |
| |
The presence of a single hard nodule in an otherwise diffusely enlarged gland, or a number of hard nodules suggest the possibility of malignancy and therefore the need for exploration and if necessary surgery. |
|
|
 |
|
Auricular fibrillation in toxic goitre is no bar to surgery provided that the preliminary detoxication has been thorough. If the cardiac impairment is due to hyperthyroidism as it often is, thyroidectomy will cure this irregularity. |
| |
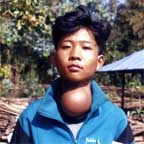
1. When there are signs of compression |
|
|
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
2. when thyrotoxicosis supervenes on a nodular goitre, secondary toxic goitre |
| |
3. when primary toxicosis do occur |
|
|
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
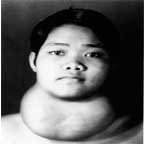
4. when there is malignant transformation of the goitre |
| |
5. when it need for cosmetic reasons |
|
|
 |
|
| |
|
|
|
6. a large firm nodular goitre with possible retrosternal or retropharyngeal extensions and existence or threat of pressure phenomenon, especially indicate the need for surgery. |
| Thus surgery of the thyroid is the most satisfactory operation giving as it does, immediately relieve with brief disability. Therefore surgery could not be overruled and still remains the ideal treatment for goitres.
. From 1964 till 2005, I have completed over 2300 cases of goitre operations for different types of goitres at different locality as esbelow.
. 1964 in Mandalay General Hospital
. 1965 - 1971 in Khamti District ( Naga Land )
. 1971 - 1978 Phyu
. 1978 in Bassein - mobile surgery in this area as DYAD
. ( Pyin Kha Yaing, Nga Pu Daw, Pathein, Athoke, Ye-Kyi, Nga Thaing Chaung, Kyaung gone, Kyone Pyaw, Hinthada )
. 1978 - 1984 in Namkham ( Northen Shan State ) The Seagrave Hosp:
. 1984 - 1987 - Mandalay Railway, Ywa Htaung, Myitngae
. 1988 - Tharawaddy
. 1988 - Pyin Oo Lwin
. 2000 - Taung Gyi, Yangon
. 2001 - upto now - Pyin Oo Lwin |
MORTILITY |
1. local shock in Namkham ( because of procaine hydrochloride 2% ) - 1 case
2. cardiac arrest on the table ( toxic goiter ) - 2 cases
3. self induced asphysia in Naga ( pulled out the plaster forcefully ) - 1 case
4. toxic goitre after local injection sets into fits and cardiac arrest ( because of procaine hydrochloride 2% ) - 1 case
5. toxic goitre during operations sets into fits and tachycardia and expired before completing surgery - 3 cases |
THYROIDECTOMY UNDER LOCAL
|
Different procedure of thyroid or goitre operation are as follows.
. 1. eneucleation of adenoma solitary
. 2. partial excision of solid adenoma
. 3. hemithyroidectomy
. 4. subtotal thyroidectomy
. 5. total thyroidectomy
. 6. ligation of superior thyroidal artery and vein and ligation of inferior thyroidal artery if impossible for removal.
. During the early years of my thyroid surgery I use to perform enucleation or partial excision of solid solitary adenomas. Also for unilateral solitary adenomas, partial thyroidectomy or hemithyroidectomy done.
. But so sorry to say the recurrent goitre do occur for at least 10% and come back for another operation.
. The word recurrent goiter is a misnomas for the new goitre arise from the remnants of thyroid tissue that you leave behind.
|
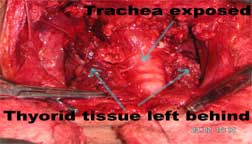
Thus I have change my surgical procedure for all my cases in the later period by using the method as bilateral subtotal thyroidectomy with barring of trachea and ligating the inferior thyroidal arteries on both side leaving only a small portion of thyroid tissue which will be necessary for his or her hormonal action. |
 |
|
PRE-OPERATION PREPARATION
After routine check up for his or her physiological function clinically no other special investigation is necessary for surgery.
The most important preoperative preparation is the postural exercise. |
The posture exercise is given three times a day under strict supervision.
The postural exercise is to lie still with both hands kept close to the body, without pillow and keeping the head slightly extended for 3-4 hours.
The reason for this exercise is that the patient is fully conscious during operation he needs to keep himself still throughout his operation period.
But during the operation period he will be allowed to drink water, lime juice if he feels thirsty and he will be allowed to speak about his feelings and will also be allowed to communicate with his/her relative who will be allow to witness the whole operation in the operation room.
The only thing that is not allow to do is to move his head nor his extremities.
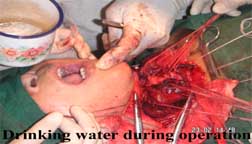 |

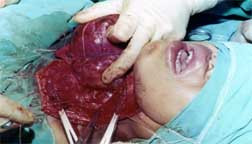
|
|
PREMEDICATION
Injection phenobarbitone sodium 200mg is given in order to allay anxiety and keep him relax ( sedation ).
Injection burmeton ( chlorpheniramine 10mg ) is given as permedication so as to prolong the action of lignocaine.
Injection pethidine or morphine is not use for it may induce respiratory depression, nausea and vomiting. I have lost one case . without putting my knife on her.
DRIP NFUSION, BLOOD TRANSFUSIONI
Since avascular surgery is practiced no drip of any kind and no blood transfusion is needed in all my cases, during and after.
FOR TOXIC CASES
Detoxication is carried out by neomercazole and inderal for increase heart rate.
|
I myself, act as an anaesthetist for local injection and as a surgeon. Sometimes if huge gigantic goiter with one doctor as assistant and one nurse and a runner or helper. If for ordinary goiter, I myself and two nurses and one runner or helper. In otherwords a team of 4 will be suitable for my surgery |
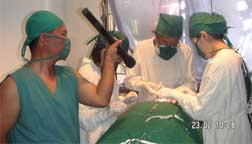 |
|
LOCAL ANAESTHESIA FOR CERVICAL PLEXUS BLOCK |
An adequate field block satisfies both the surgeons and the patients.
Intelligent use of local anaesthesia is dependent on accurate knowledge of the anastomic relations of nerve trunks to bony landmarks and important surrounding structures.
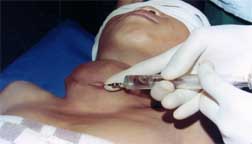 |
|
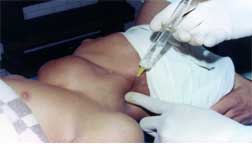
|
|
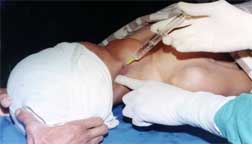
THE BEAUTY OF LOCAL ANAESTHESIA
|
1. Patients are fully conscious during operations.
2. apart from being dulled or sentitive to pain they are normal in physiological functions.
3. during operations they can constantly strengthen their confidence in overcoming the disease.
4. under local the surgeon can freely talk to the patient to determine the condition of vocalization so as to avoid inadvertently damaging the nerves controlling the vocal functions.
. 5. in practice, it has abundantly proved that this local anaesthesia method is safe, simple, economical and effective and could be practiced by ordinary doctors where facilities are not available or limited.
. 6. after operation and back in the ward patient could eat and drink immediately without difficulty.
7. under local, patient is fully conscious before, during and after operations.
8. complications of anesthesia such as infection of respiratory tract, pneumonia and others never occurred. |
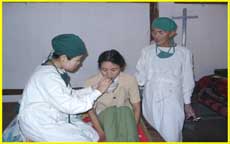
|

9. after operation he/she can put his/her clothes on, got off from the bed without help and walked about and could also eat and drink on the day of operation.
10. worries, anxieties, excitements, nervousness of the relatives is totally wiped out by his action and condition seen immediately after operation.
|
|
|
CERVICAL PLEXUS BLOCK |
|
|
I have operated all my cases under cervical plexus block which is very much effective and safe for all the patients. |
|
|
| ANAESTHETIC AGENT AND EQUIPMENT |
Lignocaine 50cc 1% without adrenaline is used in all my cases.
Maximum dose : 50cc 1%
Onset of effect : within 5-10 minutes
Duration of action : 2-4 hours if correct injection is done.
Over dose of lignocaine however can cause convulsion although this is often proceeded by somnolence rather than by excitement
|
|
|
|
|
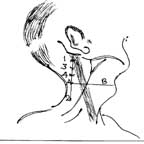
LAND MARK FOR CERVICAL PLEXUS BLOCK |
Site 1 - 1cm posterior and caudal to the mastoid process.
. Site 2 - chassaignac's tubercle, which is easily felt in a majority of subjects.
Project an imaginary straight line A between site 1 and 2. Locate the upper border of the thyroid cartilage and project a line B posteriorly until it cuts the line A.
This point of intersection marks the transverse process of the 5th cervical vertebra.
Divide the distance between site 1 and this process into three equal parts raising a skin wheal.
Points 1-3-4 mark the location of the transverse process of 2nd, 3rd, 4th cervical vertebrae.
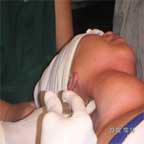 
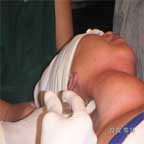
Inject 5cc of 1% lignocaine as the needle is held lightly in contact with the transverse process of each of the last named three vertebrae.
Repeat the same procedure for the opposite site.
Inject an intradermal wheal for the skin incision from one anterior border of sternomastoid to the opposite side
|
|
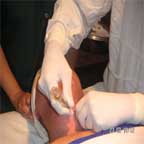
Blood vessels in the neck are large and numerous, injections in this region should be done carefully and by practice.
The patient lies in the dorsal position with or without small pillow under the shoulder blade or if not ask the patient to slightly extend the neck and the face turned away for the side requiring field block.
Not to move the head, he is kept in position by the assistant nurse while giving field block.
|
|
|
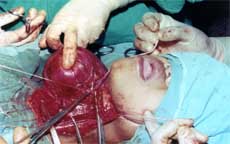
| ARRANGEMENT OF ASEPTIC TOWELS |
|
|
Two sterile towels, one quadrangular and one's triangular on top of it are slipped and held beneath the head and neck from above as the head is held in position by the staff nurse.
The uppermost triangular towel is bound firmly over the head in order to cover the chin, face and eyes keeping the nose exposed.
Laheys pad is then tucked into the space on either side of the neck. ( nape of the neck )
Head is also kept fixed in position by two sand bags one on either side of the heads. A large towel, having a rectangular section cut out above to expose the field of operation covers the whole length of the body and head.
No shoulder bridge is used to prevent discomfort of the patient.
|
|
|
STEP OF OPERATION |
Kocher transverse incision is used.
. The position and length of the incision depends upon the size symmetry and fixity of the goiter. It is planned to give the most adequate exposure consistent with the best possible cosmetic result.
It must be remembered that, with the neck fully extended and already prominent owing to the goiter, the incision must be made at a level higher than that planned for the end result. Otherwise it will be found to lie too low after the operation being then over the manubrium sterni where it will be more noticeable and more likely to become adherent.
Therefore the aim of the incision is that if a girl wearing a necklace it would have cover the line of incision.
The line of incision should extend from one anterior border of sternomastoid to the opposite anterior border of sternomastoid.
It should have the convexity downward and 1/2 inch above the suprasternal notch or more according to the size of goiter and parallel to both the clavicles.
You cut the skin, subcutaneous, platysmus all in one layer with an even pressure.
Ligate the bleeding anterior superficial veins
|
|
|
|
|
REFLEXION OF THE SKIN |
|
|
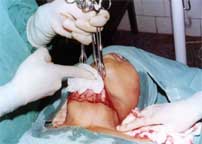
The skin and superficial fascia and the platysmus are dissected upwards and towards the skin by pulling the edge of the skin flap with 3 lanes tissue forceps and pressing or separating the underlying layer with gauge and finger dissection. No knife or scissor are used for this.
The same procedure is used to reflect the lower skin flap
Then fixed the upper and lower skin flaps with stay suture anchoring the drapper of chest and drapper of head. This way is far better than using Joll's retractor.
|
|
|
LIGATION OF VEINS
The anterior superficial jugular veins are then ligated by stay suture.
OPENING THE INVESTING LAYER
|
A longitudinal incision is then made and the deep investing layer and the infrahyroid muscles are separated from pretracheal fascial. Open the anterior border of sternomastoid sheath longitudinally.
Having made an opening in the middle of its length introduce two Kocher forceps and clamped the deep investing fascia, infrahyoid muscles all in one layer and cut between the two clamps.
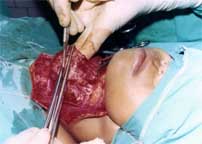
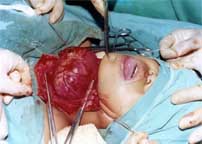
|
|
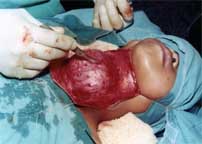
Insert 3 stay suture below the Kocher forcep to use as a retractor for further dissection.
Repeat the same procedure for the opposite side.
Now the goiter exposed and faced you for further dissection |
|
|
TO ISOLATE THE GOITRE FROM ITS BED |
Using round bodied 1/2 circle needle ligate the veins that you see on the goiter so as to prevent blood flow from one pole to the other and to use the ligature for uplifting the goiter while dissection is done.
While holding the ligatures by your assistant you dissect the middle thyroidal vein if not seen you dissect and ligate whatever vein or artery that is superficial.
( Deal with what you see first should be practiced ).
In short, you identify, dissect and ligate the superior thyroid artery and vein. Ligate the inferior thyroidal veins of lower pole.
You lift the goiter from its bed and identify dissect and ligate the middle thyroidal vein which drains into internal jugular vein.
Identify the parathyroid gland and keep it untouch. Having identify and ligated the visual vessels including superior, inferior and middle vessels, ligate and cut the superior and isolate the upper lobe and remove from its bed.
Having identify and ligate and cut the superior thyroidal arteries and veins. Look for laryngeal branch of superior thyroidal artery and vein ligate and cut so as to open the cricothyroid space.
Then deal with the pyramidal lobe and separate the isthmus which lies above the anterior surface of trachea and connects the right and left lobe of goiter by inserting pieces of trees or pieces of gauges.
Excise the goiter of left and right removing at least 3/4 of its lobe leaving the capsule and small portion of thyroid tissue an each side.
Having remove the enlarged goiter the raw edges of the remaining thyroid is resutured by interrupted suture.
Test the voice while dissecting to open the carotid gutter in order to ligate inferior thyroidal artery.
|
|
|
|
|
CLOSING BACK THE WOUND |
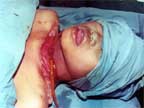
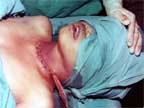
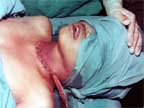
|
|
1. Recheck the presence of parathyroid.
2. Recheck the vocalization by asking the name.
3. Look for bleeding points.
4. Recheck the ligatures of superior, inferior and middle thyroidal veins.
5. When everything is safe and ok insert a corrugated rubber drainage tube beneath the infrahyoid muscles.
6. Resuture the infrahyroid muscles with deep investing layer all in one layer for both side.
7. It is not necessary to resuture the infrahyoid and deep investing layer in the middle.
8. Then place a rubber glove drainage beneath the skin flap.
9. Resuture the skin flap by interrupted suture.
10. Clean the neck and incisional area and apply a pad above it before strapping with the plasters.
11. Then ask the patient to get up and walk back to its bed.
12. Immediately on arrival, allow to take hot noodles or soup or tea and bread whatever he/she prefer to eat. |
|
|
IMMEDIATELY AFTER OPEREATION |
Thus patient is allowed to walk in, into the OT room and walk back after operation to his/her bed.

|
|
|
|
|
POST-OPERATIVE TREATMENT
After 24 hours of post operation 1st dressing done and the two drainage tubes removed. Reapply sterile pad on incision and strap the wound by adhesive plaster around the neck.
On 4th or 5th or 7th day according to the improvement, remove the stitch. For postoperation treatment no blood, no infusion, no injection is given. Only oral antibiotic given for 7 days.
This is the best method for thyroidectomy. It is safe, sound and good but the surgeon should not be drastic. No pulling, pressing should be done. You must be gentle and thorough.
DIFFICULTIES AND DANGERS OF THYROIDECTOMY
While dissecting the upper pole of thyroid for ligation of superior thyroidal artery and vein you must not exert forcible retraction the pedicle may be torn.
To avoid or prevent its occurance you ligate the superior pole by stay suture and open the cricothyroid space by ligating and cutting the laryngeal branch of superior thyroidal vessels.
Then by dissecting and finding the inferior border of upper pole you insert a ligature and tie the superior thyroidal vessels away from the thyroid upper pole.
Multiple lateral thyroid veins may be present. Therefore carefully isolate and ligate.
Short lateral veins may be present. Therefore careful dissection and ligation should be done.
Short inferior thyroid veins may be present in cases of retrosternal or retroclavicular prolongation. To ovoid this clean and gentle dissection is important before isolation of prolongation.
In toxic goiter adherent may be noticed. The thyroid is also very friable and vascular in nature. Therefore proper detoxication should be done.
WARNING
It is said that the most difficult operation in the human body is thyroid operation. It may be true because the thyroid gland act like a vascular shunt. All the blood that the brain needs passes or travels through the thyroid gland. The whole volume of blood that is present in the human body travels through the thyroid within an hours time.
. The thyroid gland and its tumor looks nothing difficult because it is visible and prominent in the neck and you can also feel easily. . . The vascular set up is also simple and consist of two inferior, two superior and one middle thyroidal vein one on each side as a main trunk. The arterial supply also is superior, inferior thyroidal artery as a main trunk and on each side.
. Laryngeal, pharyngeal branches are small and unnoticeable. The biggest common carotid artery and internal jugular lies in the carotid gutter of each sides. But though seems to be easy it actually is the most difficult surgical operation of the human body.
. So if you have intention to operate I would advice you to be cool, stable, tactful and be careful not to pull by force in your manipulation.
. Use all the essence of the surgeon i.e .
. 1. Heart of the lion
. 2. Hands of the lady
. 3. Eyes of an eagle
. 4. mouth of an angel
. The last but not the least REMEMBER if you intend to operate a goiter, you and your patient is marching towards the graveyard hand in hand. |
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
|
|
|
|
<< BACK |